What is the #NUM! Error?And how to fix it
Excel has tons of functions that you can access through the use of formulas.
Many of these functions involve numbers such as the various mathematical, statistical, and financial functions (e.g. SUM, SQRT, STDEV, IRR, etc.).
These functions ease the burden of having to do so many calculations.
That said, they typically only properly work if they’re being used correctly.
If you use these functions a lot of times, you’ll know what I mean.
If the conditions to make these functions work aren’t met, they’ll return an error value.
One such value is the #NUM! error.
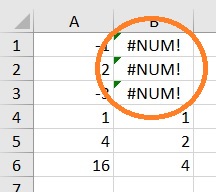
How does the #NUM! error occur?
What does it mean? And what can you do to fix it?
In this article, we’ll be answering these questions.
We’ll be exploring what this particular error is and why it happens.
By the end of the article, you should have a deeper understanding of the #NUM! error value.
Let’s get started.
What is a #NUM! Error?
#NUM! error is an error value that appears in Excel.
It typically occurs when you enter a formula in a cell, but Excel cannot perform the calculation.
In other words, Excel cannot execute the formula properly. There are several reasons why this could happen.
For example, the formula you’ve entered may be an impossible mathematical equation.
By that, I mean that the formula may be computing the square root of a negative number, which is mathematically impossible.
Even with the help of Excel, one cannot calculate the square root of a negative number because it does not exist.
Let’s go over the possible causes of a #NUM! error occurring and how to fix it.
Why Does #NUM! Error Occur? (And How to Fix It)
There are four reasons why a #NUM! Error occurs:
- The resulting number may be too big or too small for Excel to handle
- The formula is trying to perform an impossible mathematical equation
- An iterative formula cannot find a result
- You’ve entered an incorrect function argument
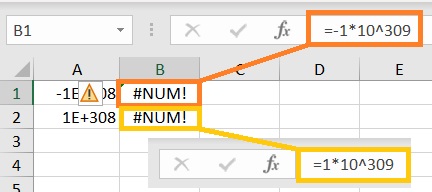
The Resulting Number May Be Too Big Or Too Small For Excel To Handle
While Excel is a powerful piece of software, it still has its limitations.
The smallest number it can handle is -1*10^308 (or -1 followed by 308 zeros), while the largest number it can handle is 1*10^308 (or 1 followed by 308 zeros).
Any number that is lower or higher than these limits will result in a #NUM! error.
How to Fix This?
Unfortunately, there’s no way you can make Excel display a number that is beyond its limits.
Your only recourse in this situation is to change the input (for formulas) or output.
The Formula Is Trying To Perform An Impossible Mathematical Equation
An impossible mathematical equation will still be an impossible mathematical equation even if you attempt to perform it in Excel.
Since Excel cannot return a number, a #NUM! error will occur.
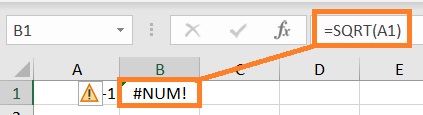
Just like in the illustration above. The formula is attempting to calculate the square root of -1, a negative number.
But since calculating the square root of a negative number is impossible, the formula returns a #NUM! error value.
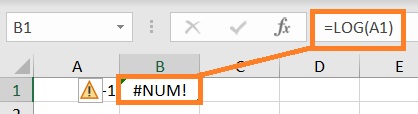
Calculating the LOG of a negative number also results in a #NUM! error value.
How to Fix This?
You either have to change the negative number into a positive one, or you can use its absolute value.
The absolute value of a number is a measure of how far it is from zero. -1 and 1 have the same absolute value, which is 1.
You can use the ABS function to calculate the absolute value of a number.
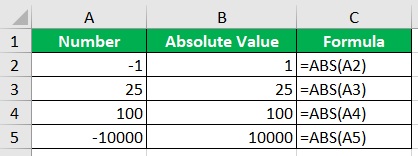
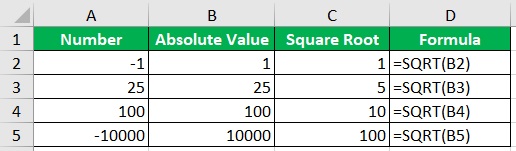
Since absolute value is not a negative value, you can use it to calculate the square root or LOG.
An Iterative Formula Cannot Find A Result
There are some Excel functions that rely on iteration to find a result.
Examples include the IRR, RATE, and XIRR functions.
These functions rely on iteration to find the most accurate answer (down to the very last 0.0001%).
The thing is, Excel limits the number of iterations these functions can do. This is for performance reasons.
If Excel allows an unlimited number of iterations, it may enter into an endless loop.
If Excel cannot find the answer after exhausting its limited number of iterations, a #NUM! error will occur.
How to Fix This?
You can increase the number of allowed iterations.
By default, the maximum number of iterations is 100.
But you can increase it if you need to.
- Open the File Tab. This will open the File menu.
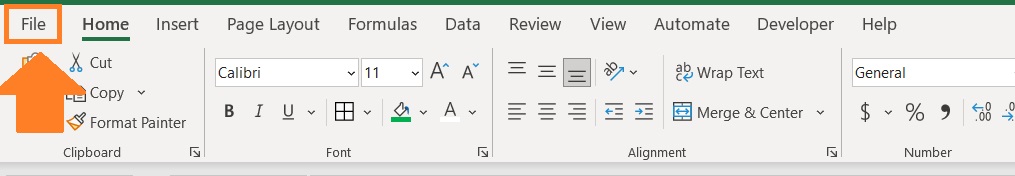
- In the File menu, click on Options (found at the very bottom) to open the Excel Options dialog box.

- In the Excel Options dialog box, select Formulas. On the right side of the menu, you should a section regarding iterative calculations. You can increase the maximum iterations here (the default is 100).
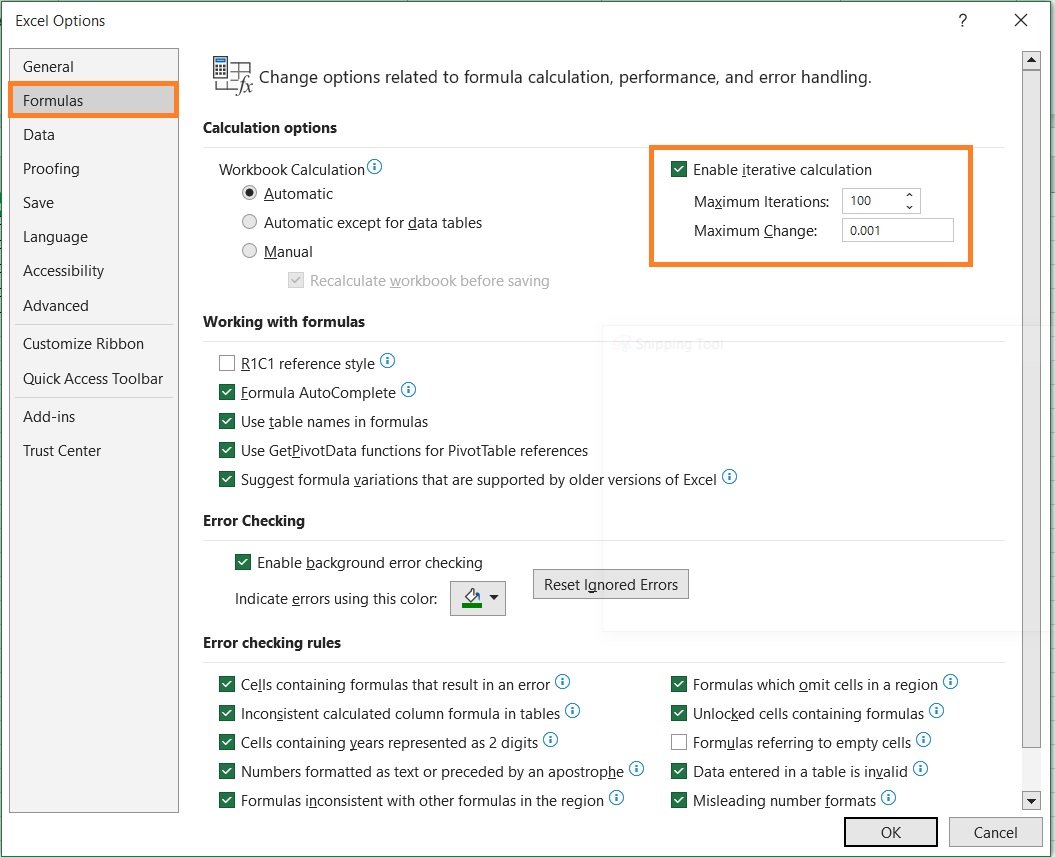
Do note that by increasing the maximum number of iterations, you may experience a noticeable drop in performance whenever using iterative formulas.
You’ve Entered An Incorrect Function Argument
Each Excel function requires the proper arguments for it to work.
For example, for the IRR function to work properly, there must be at least one negative and one positive value.
If the numbers are all positive, the IRR function will return a #NUM! error value. The same thing will happen if the numbers are all negative.

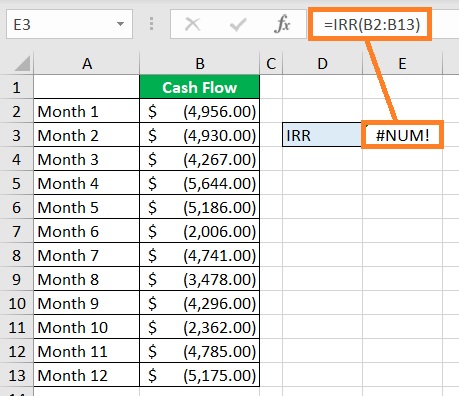
How to Fix This?
This is easy. You only need to fix the faulty argument.
In the case of the IRR function, you need to make sure that there is at least one negative and one positive value.
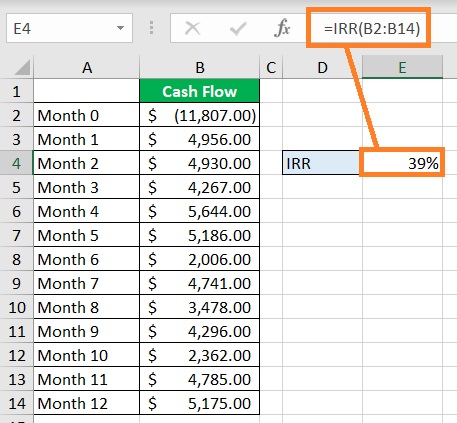
To avoid this kind of error from happening, you must have a great understanding of the functions that you’re using.
Make sure that you’re using the correct arguments that the function requires.
Conclusion
Do you have a deeper understanding of the #NUM! error?
In this article, we were able to discuss the different reasons that may cause this particular to occur.
Along with that, we have discussed the fixes.
You should be able to address any #NUM! error from now on.
