Removing a Specific Character From a String in ExcelLearn how to clean your data in Excel with these features and functions
When you import data to Excel from another application, you’ll probably have to do some cleaning before you can properly work with the imported data.
This usually involves removing unnecessary spaces, deleting unwanted characters, properly lining up the data, etc.
While you can do the clean-up manually, it’s not the most efficient way of doing things.
Just take a look at this:

The above example isn’t even a large amount of data, but just by looking at it, you’ll know that it’ll take time to manually clean it.
Can you imagine if you do so with a large amount of data? I’m talking about hundreds, thousands even!
Thankfully, Excel has tons of nifty features and functions that you can use to clean your data.
In this article, we will be learning how to use these features and functions to clean your data.
We’ll be learning how to remove a specific character from a string.
We’ll also be learning how to remove unnecessary spaces as well as unwanted invisible characters.
By the end of the article, you should be able to reliably remove unnecessary and unwanted characters from any string.
Let’s get started.
Use the Find and Replace Feature to Remove a Specific Character in Excel
Find and Replace is an Excel feature that we can use to replace a specific value with a new value.
We can use it on a cell or a group of cells. It can be accessed in two ways: (1) Open the home tab, then click the Find and Select button (somewhere to the left of the ribbon) and select Replace from the options; (2) press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + H.
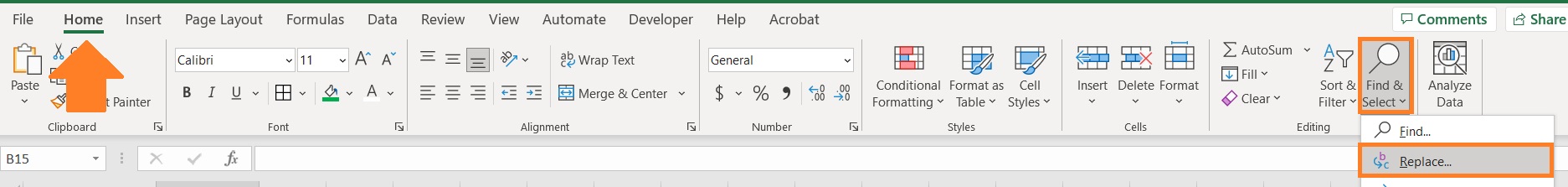
Both actions will open the Find and Replace dialog box, with the Replace tab opened.
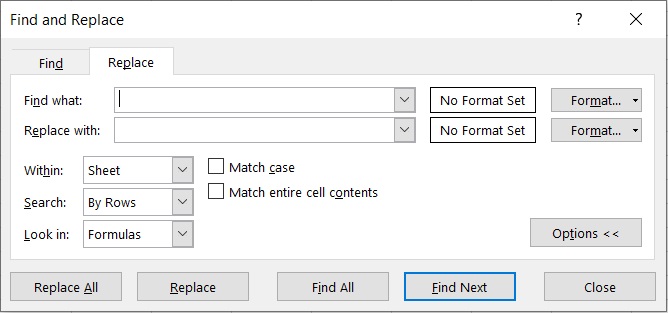
The notable features for us here are the textboxes after “Find what” and “Replace with”.
We’ll be inputting the value that we want to replace in the textbox after “Find what”.
In the textbox after “Replace with”, we’ll be inputting the new value that will replace the old value.
We can use this feature to replace a specific character with a blank, essentially removing it from our selection.
Remove a Specific Character in Excel
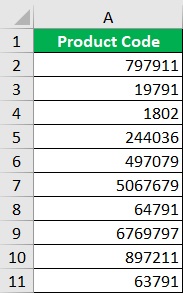
Suppose you are to work with the following data:
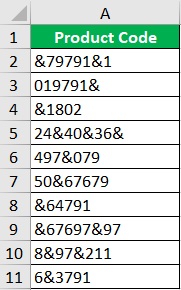
Per inquiry, this dataset should only include numerical values (aside from the column header).
As such, you’d have to remove unnecessary characters from the data strings (which is the character & in this case).
- Select the cells from which you want to remove a specific character.
- Open the Find and Replace dialog box. To do so, open the home tab, then click the Find and Select button (somewhere to the left of the ribbon) and select Replace from the options. Alternatively, you can press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + H.

- In the Find and Replace dialog box, make sure that the Replace tab is opened.
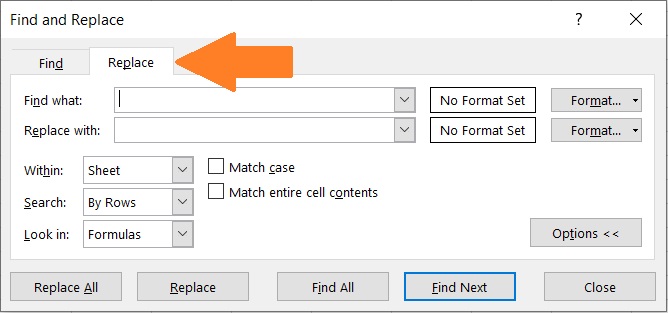
- In the textbox after “Find what”, enter the character that you want to remove (which is the character “&” for this example).

- In the textbox after “Replace with”, make sure to leave it blank.
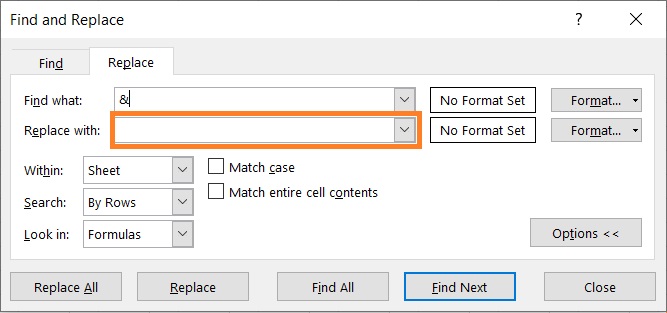
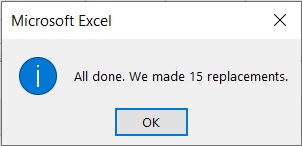
- Click the Replace All button. This will remove the specific character from your selection. Excel will also notify you of how many replacements it made.

- Close the dialog box. The specific character should now be removed from your selection.
Do note that this feature directly modifies the original value.
If you want to retain the original value, you may want to make a copy before using the Find and Replace feature.
You can also look into the other methods of removing a specific character from a string.
Use the SUBSTITUTE Function to Remove a Specific Character in Excel
The SUBSTITUTE function allows us to replace a specific character (or string) from a string with a new value.
We can also use it to remove the specific character (or string) by replacing it with a blank.
Unlike the previous method, the result from the SUBSTITUTE function will show in another cell.
This means that the original value will be untouched.
The formula for using the SUBSTITUTE function is as follows:
=SUBSTITUTE(original_string,old_value,new_value,instance_number)
Where
original_string – refers to the string from which you’ll remove the specific character from
old_value – refers to the value (specific character) that you want to replace or remove from the string
new_value – refers to the value that will replace old_value. To remove old_value instead, you can specify new_value as blank (set it to “”)
instance_number – this specifics which instance of old_value will be replaced. This parameter is optional. If left blank, all instances of old_value will be replaced from the string
Remove a Specific Character in Excel
Suppose you are to work with the following data:
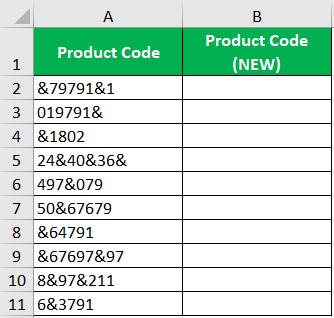
In the column with the header “Product Code (NEW)”, you are to make a copy of the old product code but with only the numerical values.
This means that you have to remove non-numerical values from the strings. To do so, you’ll be using the SUBSTITUTE function.
- Select a blank cell where you want to display the result. Ideally, you’d want this cell to be adjacent to the cell that contains the string that you want to remove a specific character from. (For our illustration, we will be selecting cell B2).
- In the selected cell, enter the formula for the SUBSTITUTE function. In our illustration, we want to remove the “&” character as it is the only non-numerical value from the string. And since we want to remove it, the formula will then be =SUBSTITUTE(A2,“&”,“”).
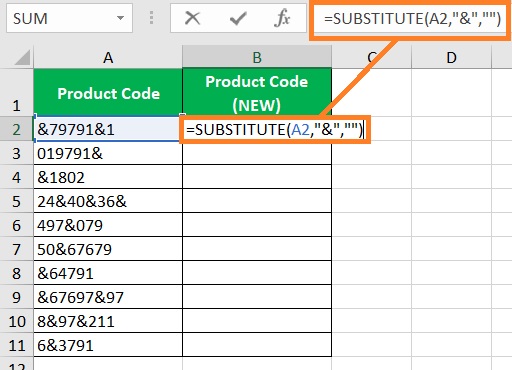
- Press the Enter This should remove the specific character from the string.
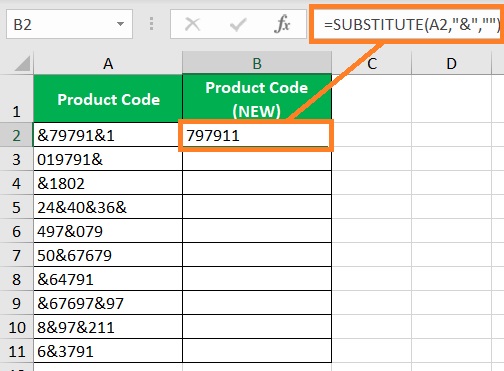
- Copy the formula to the rest of the column (until the next empty row).

Do note the result will always be treated as a text string even if it only contains numeric values.
If you want the result to be treated as number, you may modify the formula by adding *1 at the end (e.g. SUBSTITUTE(A2,“&”,“”)*1)).
Make sure that the string only contains numeric values.
Remove Several Characters From a String
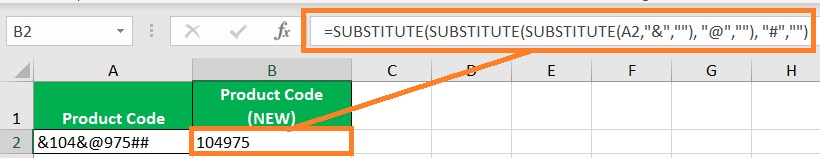
If there are more than distinct characters that you want to remove from a string, you can just nest several SUBSTITUTE functions for each character. For example, you want to remove non-numerical values from the following:

Here, the non-numerical values that you want to remove are “&”, “@”, and “#”. We can nest several SUBSTITUTE functions to remove them. The formula will be:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(A2,”&”,””), “@”,””), “#”,””)
Use the REPLACE Function to Remove a Specific Character in Excel
The REPLACE function (not to be confused with the Find and Replace feature) allows us to replace a specific character or string from a string based on where it is placed (on the string).
This is useful if the character that you want to remove from the dataset is placed constantly.
For example, it is always the first character of the data.
The formula to use the REPLACE function is as follows:
=REPLACE(original_string, start_num, num_chars, new_value) is a powerful Excel function that lets you substitute part of a text string with new content. You simply choose where to start in the original text, how many characters to replace, and what you want to insert instead, making it ideal for quickly updating or cleaning large sets of data.
Where
original_string –– refers to the string from which you’ll remove or replace the specific character from
start_num – specifies the position of the character or string in original_string that you’ll be replacing or removing
num_chars – specifies the number of characters in original_string that you’ll be replacing or removing
new_value – refers to the value that will replace the specified character/s. To remove the character/s instead, you can specify new_value as blank (set it to “”)
Remove a Specific Character in Excel
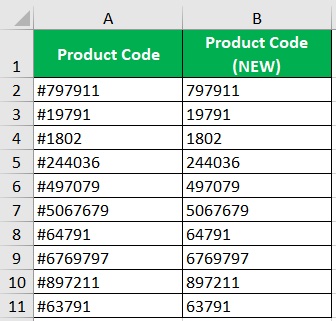
Suppose you are to work with the following data:

In the column with the header “Product Code (NEW)”, you are to make a copy of the old product code but with only the numerical values.
This means that you have to remove non-numerical values from the strings, which are the #s at the beginning of each string.
To do so, you’ll use the REPLACE function.
- Select a blank cell where you want to display the result. Ideally, you’d want this cell to be adjacent to the cell that contains the string that you want to remove a specific character from. (For our illustration, we will be selecting cell B2).
- In the selected cell, enter the formula for the REPLACE function. In our illustration, the character that we want to remove is the # at the beginning of each string. The formula will then be =REPLACE(A2,1,1,“”).

- Press the Enter This should remove the specific character from the string.

- Copy the formula to the rest of the column (until the next empty row).
Do note the result will always be treated as a text string even if it only contains numeric values.
If you want the result to be treated as a number, you may modify the formula by adding *1 at the end (e.g. REPLACE (A2,1,1,“”)*1)).
Make sure that the string only contains numeric values.
Use the TRIM Function to Remove Leading and Trailing Spaces
Most data cleaning will consist of removing excessive spaces from strings.
Sometimes, you may only have to remove those unnecessary spaces. With Excel’s TRIM function, you can remove them swiftly and easily.
What this function does is that it removes leading and trailing spaces.
There’s a space before the string? TRIM will remove it for you. There are extra spaces in between the string? TRIM will also remove them for you.
The formula for using the TRIM function is as follows:
=TRIM(original_string)
Where
original_string –– refers to the string from which you’ll remove excessive spaces from
Remove Extra Spaces in Excel
Suppose you are to work with the following dataset:
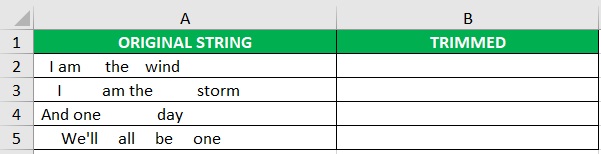
As you can see, there’re tons of unnecessary spaces. Your goal here is to remove those extra spaces.
To do so, you’ll use the TRIM function.
- Select a blank cell where you want to display the result. Ideally, you’d want this cell to be adjacent to the cell that contains the string that you want to remove a specific character from. (For our illustration, we will be selecting cell B2).
- In the selected cell, enter the formula for the TRIM function. In our illustration, the formula will be =TRIM(A2).
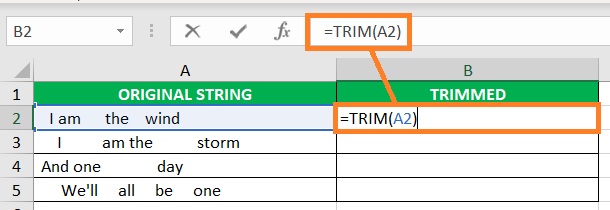
- Press the Enter This should remove the extra spaces from the string.
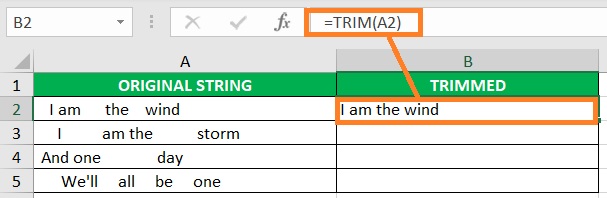
- Copy the formula to the rest of the column (until the next empty row).

Use the CLEAN Function to Remove Any Special Character
If you have to remove line breaks and other non-printable characters from a string, then the CLEAN function works best for you.
It removes the first 32 non-printable characters in the 7-bit ASCII code (those with values 0 to 31).
Do note that non-printable characters that have values of 32 or higher will not be removed by the CLEAN function.
The formula for using the CLEAN function is as follows:
=CLEAN(original_string)
Where
original_string –– refers to the string from which you’ll remove line breaks and other non-printable characters
Remove Invisible Characters from A String in Excel
If the TRIM and CLEAN functions don’t remove particular spaces, it could be that there are invisible characters in the string.
These invisible characters are most likely non-breaking spaces, which have a character value of 160.
To remove these non-breaking lines, you will have to use the following formula:
=SUBSTITUTE(original_string,CHAR(160),“”)
Where
original_string –– refers to the string from which you’ll remove line breaks and other non-printable characters
Conclusion
And those are the different features and functions that you can use to clean your data.
You should now be able to reliably clean the data that you’re working on any time you have to.
