Quarterly CompoundingDefined along with Formula & How to Calculate
What is Quarterly Compounding?
Quarterly compounding refers to the process of computing for the interest earned quarterly on a fixed deposit or investment, computed based on the principal amount plus the interest earned for previous periods.
The process of compounding interests is especially beneficial for banks that offer interest income on deposits computed quarterly, or it could also be used to calculate interest earned on other financial instruments.
Quarterly Compounding Formula
The Quarterly Compounding Formula is
Cq = P [ (1+r)4*n – 1 ]
Where:
Cq = Quarterly Compounded Interest
P = Principal Amount
r = rate of interest
n = number of periods
The quarterly compounding formula is taken from the compounding formula.
The only difference is that the rate of interest is raised 4*2 to reflect the quarterly computation of the interest.
Examples
Example # 1
Jane Smith deposited $25,000 in AA Community Bank for 3 years. The bank pays 3.5% interest, compounded quarterly.
From the statement above, the following are the information available:
Principal Amount – $25,000
Rate of Interest – 3.50%
Number of Years – 3
Frequency – 4
To calculate the Quarterly Compounded Interest with the formula provided, it will be:
Cq = P [ (1+r)4*n – 1 ]
Cq = $25,000 [ (1+3.5%/4)4*3 – 1 ]
Cq = $25,000 [ (1.00875)12 – 1 ]
Cq = $2,755.09
To compute this using Excel, the formula will look like this:

Example # 2
Jane Smith has invested $100,000 in ABC Corporation which will be invested in two phases: Phase I requires that 50% should be invested for the first 3 years, and the remaining amount shall be invested in the next three years (Phase II).
During Phase I, the investment will earn an interest of 7.5%, while in Phase II, it will earn an interest rate of 7.9%.
The above information can be presented in a table to easily derive the information needed to compute for the investment income.
| Phase I | Phase II | |
| Principal | $50,000.00 | $50,000.00 |
| Interest Rate | 7.50% | 7.90% |
| Frequency | 4 | 4 |
| Number of Years | 3 | 3 |
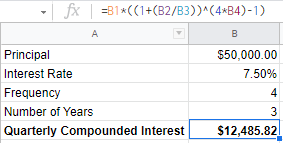
Phase I
Cq = P [ (1+r)4*n – 1 ]
Cq = $50,000 [ (1+7.5%/4)4*3 – 1 ]
Cq = $50,000 [ (1.01875)12 – 1 ]
Cq = $12,485.82
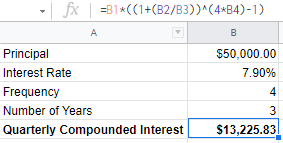
Phase II
Cq = P [ (1+r)4*n – 1 ]
Cq = $50,000 [ (1+ (7.9%/4))4*3 – 1 ]
Cq = $50,000 [ (1.01975)12 – 1 ]
Cq = $13,225.83
Total Investment Income is therefore $25,711.65 computed as the sum of the Quarterly Compounded Interest for Phase I ($12,485.85) and Phase II ($13,225.83).
Relevance and Uses
Compared to simple interest, compounding allows money to grow more quickly.
Compounding is not limited to quarterly compounding – monthly, semi-annual and annual compounding can also be applied.
However, the most common compounding periods for financial products, including savings, are quarterly and semi-annually.
FundsNet requires Contributors, Writers and Authors to use Primary Sources to source and cite their work. These Sources include White Papers, Government Information & Data, Original Reporting and Interviews from Industry Experts. Reputable Publishers are also sourced and cited where appropriate. Learn more about the standards we follow in producing Accurate, Unbiased and Researched Content in our editorial policy.
Brigham Young University - Idaho "Compounding Quarterly, Monthly, and Daily" Page 1 - 8. February 16, 2022
University of Hawaii "COMPOUND INTEREST" Page 1 . February 16, 2022