Excel TRIM function – Remove Extra Spaces [Beginning, End, or Middle]Tutorial with Screenshots
The TRIM function is one of Microsoft Excel’s many Text functions, which helps to make working with text characters easier and faster.
The TRIM function does this by allowing users to remove excess spaces from datasets.
This is critical for preventing errors that occur due to the presence of hidden extra spaces.
The TRIM function specifically allows users to remove any spaces beyond a single one between words.
This can be particularly useful in situations where data is imported from other applications, which often results in irregular spacing.
This may allow an extra space to be hidden either before or after text or numeric values inside of your cells.
Hunting these spaces down individually can be difficult and, in some large datasets, virtually impossible, but with the TRIM function, it can be accomplished in seconds.
Here we will take a look at some of the uses for the TRIM function and how it can be used to remove extra spaces in Excel.
How the TRIM Function Works
The TRIM function can remove all extra spaces from cells, including leading, trailing, or multiple spaces located between values.
This means it can remove all spaces except a single one located between each word.
The syntax for the TRIM function is quite simple, specifically:
TRIM(text)
The only argument for this function is text, which is the text for which the function will remove excess spaces, and this can be entered directly within quotation marks or as a cell reference.
It is important to keep in mind that by spaces, this means the value 32, 7-bit ASCII space character from the Unicode character set.
Other types of “spaces” include the non breaking space character, which is often used in HTML web development, line breaks, as well as non-printing characters.
In order to remove some of these types of spaces, you might consider using the CLEAN function in addition to the TRIM function. For example:
=TRIM(CLEAN(A1))
This formula would allow you to remove a wider range of non-printing characters.
Now let’s take a look at how you can use the TRIM function in practice.
How To Use TRIM To Remove Trailing, Leading, or Multiple Spaces
The TRIM function exists just for removing extra spaces, such as the ones in the example below.
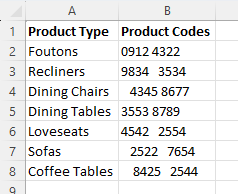
Here we have a list of product types and their associated product codes.
Though the product types do not appear to have any extra spaces, this is clearly not the case with the product codes. This issue can result in formulas such as VLOOKUP failing to return our desired results if we search by product code.
Fortunately, the TRIM function can help us to eliminate these extra spaces, and here is how.
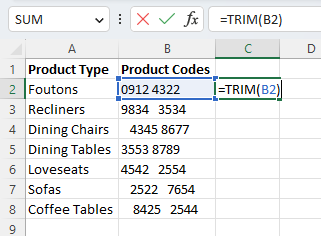
- In the column next to the cells, we would like to remove extra spaces from entering the formula =TRIM(B2). If there is no empty column next to your cells right, click the column header and select “Insert” to add an empty column.
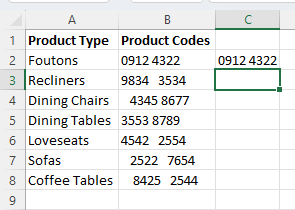
- Run the formula, and Excel will return the data contained within the original cell but without any extra spacing.
- Select the cell with the newly trimmed results and click on the fill handle on the bottom-right-hand side. Drag this handle down to the bottom-most cell in your dataset to extend the formula to the remaining data.
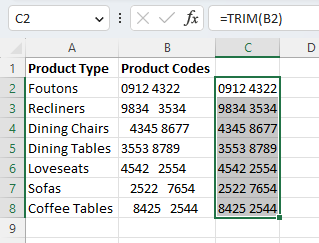
- Now you may be tempted to delete your original dataset and simply use the newly cleaned-up results, but they are still linked to the original cells. In order to simply save the results, copy your new column and use “Paste Values” from the “Paste” dropdown on the ribbon to save the results without the underlying formula.
As you can see, the TRIM function is easy to use and can quickly clean up a messy dataset with extra spaces.
However, in some cases, you may only want to remove leading spaces without affecting the rest of the dataset, and this is something that the TRIM function cannot do on its own.
Fortunately, there is a workaround that we can use to accomplish this, and we will look at that next.
How To Remove Leading Spaces Without Affecting the Rest of Your Dataset
On its own, the TRIM function is a broad tool that removes all extra spaces regardless of their location.
Generally, this is okay because, in most cases, we only want a single space between words and have no need for trailing spaces.
However, this is not always the case.
For example, we may choose to add double spaces between certain data points to enhance readability or add emphasis, and in those circumstances, we need a workaround to prevent the removal of our intended spacing.
We can do this by using a combination of the FIND, MID, and LEN functions in addition to our TRIM function.
This is the formula we will use:
=MID(B2,FIND(MID(TRIM(B2),1,1),B2),LEN(B2))
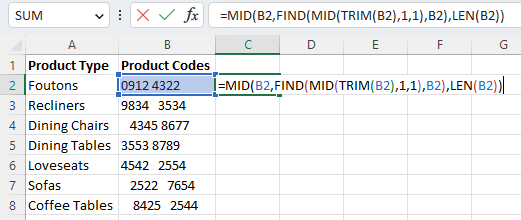
By following the same steps to enter, drag the fill handle, and “Paste Values,” we can remove leading spaces while leaving the rest of our data as is.
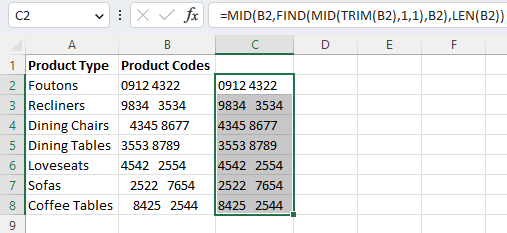
Now all of your leading spaces are removed while leaving any extra spaces in the remainder of the text.
However, there may be some circumstances in which you need to know how many spaces there actually are in the text, such as to ensure that a uniform number of spaces have been included. Next, let’s see how we can check.
How To Count the Number of Extra Spaces in Cells
In cases where we want to include a certain number of spaces, such as to double or triple space certain items, we may want to know how many extra spaces are present in our data.
To do this, we can use the LEN function.
The LEN function returns the number of characters contained within a text string, and by using it in combination with the TRIM function, it is possible to determine how many extra spaces a cell contains.
We can do this by using the LEN function to count the number of characters and then subtracting the same function without extra spaces.
To do this, we will use the formula:
=LEN(B2)-LEN(TRIM(B2))
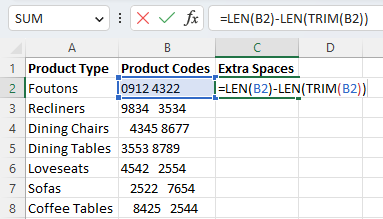
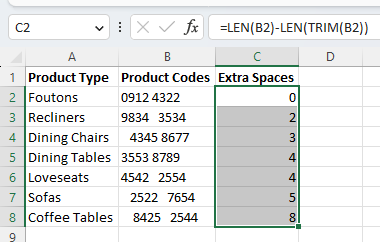
Once run, you can use the fill handle to extend it to any of the remaining cells in a row.
Conclusion
The TRIM formula is a critical tool in any Excel user’s toolbox for cleaning up datasets and removing excess spaces.
It is particularly useful when working with other users and data imported from other spreadsheet software to ensure clean and useable data.
