Easy Steps on How to Use the IF Function with Dates in Microsoft ExcelStep by Step Instructions with Screenshots
There are a lot of functions that are present in Microsoft Excel.
One of these functions is the IF function.
It uses test conditions and returns one value whether it is TRUE or FALSE.
Comparison of values is one of the most common uses of IF functions.
The values can be described as number, date, text, etc. But for the date, the application is not that intuitive.
We will exhibit some examples of how we can use the IF function in Excel with date values.
IF Function Syntax and Usage
The formula of syntax for the IF function:
| IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false]) |
Here is the breakdown of the formula:
- logical_text – the criteria that we want to test using the IF function.
- value_if_true – the value you want the test to return if the logical_test is TRUE.
- value_if_true – the value you want the test to return if the logical_test is FALSE.
For our example, if you want your value to be precisely 100 located at the A3 cell, then the value will reflect as “YES”.
But if the value is greater than or less than 100, then the value reflected in the B2 cell is “NO”. You can see our example in the image below:
| =IF(A3=100,”yes”,”no”) |
Dates Comparison in Microsoft Excel
Comparison of the operator to other values like numbers, text, etc. when we use dates are slightly different.
The table below shows the comparison of operators used for the comparison of dates:
| Sign | Denotation |
| < | Is before |
| = | Equal |
| > | Is after |
| <= | The same as or before |
| => | The same as or after |
How to Use IF Function with Dates
If you are using the IF formula for dates, it may seem similar to other numerical values or text values since they tend to use similar comparison operators. Dates are more sophisticated than that.
Excels IF functions don’t recognize dates, compared to other functions. If you test the dates using a logical test, Excel will recognize them as normal values.
If you are testing a certain date like “>12/01/2022” using the IF function, it will just simply see it as a text and not a date.
Here are examples of how you can use the IF function for your date value as logical_test parameters.
By the Use of the IF Function with the DATEVALUE Function
If you are using a date value as a logical test in your IF function, you will need to use the DATEVALUE function. By using this function, you are converting the date text format to a serial number format. Now Excel will recognize it as a date.
If you enclose the date with a quotation character, it’s basically a text value. So you need to use the DATEVALUE function to convert the date text value to the actual Excel date value.
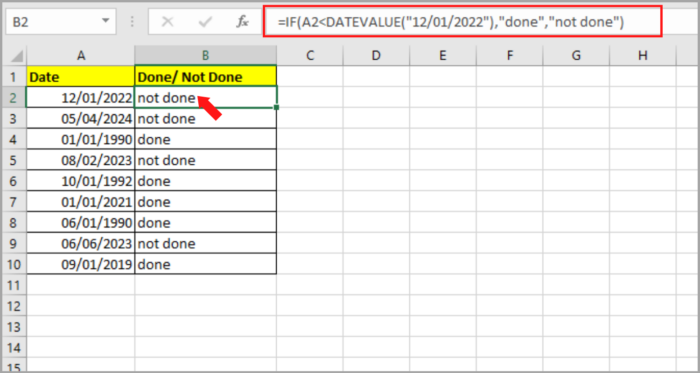
For our example, you have a given date (02/02/1995) located at cell A2 and you want to address the “done’ or “not done” in cell B2.
You will need to use the IF function incorporated with the DATAVALUE function in B2. Here’s the formula that we will be using:
| =IF(A2<DATEVALUE(“12/01/2022″),”done”,”not done”) |
Here is an example of this scenario:

By the Use of IF Function with TODAY Function
If you need to use the current date and compare it to a certain date, TODAY function is very useful and incorporates it with IF function.
For our example, you have a given date (12/01/2022) located at A2 cell and you want to address the “done’ or “not done” in cell B2, and at the same time, compare it to the current date. You will need to use the IF function incorporated with the TODAY function in B2. Here’s the formula that we will be using:
| =IF(A2<TODAY(),”done”,”not done”) |
Here is the example of this scenario where the current date is 12/01/2022:

By the Use of the IF Function with Future or Past Dates
Excel also has a lot of features that are built into it. In dates, you can implement addition and subtraction operations. You use the past dates up to January 1, 1900.
It is characterized by one whole number each day after that.
Therefore, January 02, 1900, matches up to serial number 2.
Adding n numbers to the date is the same as the n numbers of the serial numbers.
If TODAY() is 12/01/2022, therefore TODAY()+15 is fifteen days forward to the current date (12/16/2022).
Thus, TODAY()-15 is fifteen days backward to the current date (11/16/2022).
For our example, you have a given date (12/01/2022) located at cell A2 and you want to address the “within range” if it is 15 days prior to the current date in cell B2. If not, it should be shown as “out of range” in that cell.
You will need to use the IF function incorporated with the TODAY function in B2. Here’s the formula that we will be using:
| =IF(A2<TODAY()+15,”within range”,”out of range”) |
Here is an example of this scenario where the current date is 12/01/2022:

Key Points:
Here are some notes that you need to understand about using the IF function:
- As an alternative to manually typing the dates in using IF functions logical test parameters, you can record the dates on a separate cell and state them in your formulas. As a replacement for =IF(A2<”12/01/2022”,”done”,”not done”), you can just record the date 12/01/2022 in a separate cell, select B2 cell and type the formula: =IF(A2<B2,”done”,”not done”).

- Just like the explanation of the first part of the tutorial, you can also use the DATAVALUE function.

- By simply adding a zero to the date which is enclosed with parentheses, you can make your formula neat. Just type: =IF(A2<”12/01/2022”+0,”done”,”not done”). This technique makes Excel take the date (enclosed with a parenthesis) and make it as a serial number. And now, this can be used as a logical test without changing its value.

In this short tutorial, you are shown how to correctly use the IF function with dates.
Hope this helps you with your project!