How to Generate Random Numbers in ExcelUsing the worksheet functions, a Microsoft add-in, or VBA code
When it comes to Excel, most people are used to working with fixed numbers and formulas in their spreadsheets.
However, situations may arise when you need to select a random number from your worksheet.
For example, you may need random numbers to perform statistical analysis using a wide variety of financial models.
In many cases, financial models may need to be run hundreds or even thousands of times with randomized parameters.
However, in some cases, you may need to use random numbers for something as simple as picking the name of a contest winner from a list of names. The potential uses are nearly endless.
Though it may not be quite as easy as inputting the fixed data you are used to, Excel does provide users with multiple ways to generate random numbers, including worksheet functions, a Microsoft add-in, and VBA codes.
Here is how to use these methods to generate random numbers for your workbooks.
How To Use Workbook Functions To Generate Random Numbers
Excel has two different worksheet functions that can generate random numbers. These include:
- RAND: This function can give a random number with few if any, repetitions. However, it can only generate random numbers between 0 and 1, which means that it will be a decimal value.
- RANDBETWEEN: This function can give a random number that falls between two specified values. This means no decimal value; however, there is a higher potential for repeats than with the RAND function.
How To Generate Random Numbers with the RANDBETWEEN Function
The RANDBETWEEN function can be used to generate random integers within a predefined range.
The formula for this function:
RANDBETWEEN(Bottom, Top) is an Excel function that returns a random whole number between the two values you specify—“Bottom” as the lowest possible number and “Top” as the highest.
Where
- Bottom = The lower range of numbers you want to return.
- Top = The higher range of numbers you want to return.
Here is how to generate random numbers in an Excel workbook using the RANDBETWEEN function

- Select the cells where you would like the random numbers to be outputted.
- Now in this active cell, enter the text + RANDBETWEEN(Bottom, Top). The bottom and top should be replaced with the range of numbers within which you want random numbers to be generated.
- Hold down the “CTRL” key and click “Enter.”
- This will generate random numbers within the indicated range in your selected cells.

It is easy to see that this is a very easy-to-use function to generate random numbers between specified values, but it does have a high potential for generating repetitive values.
However, when this is not a concern, it is likely the easiest way to generate random values in Excel.
Keep in mind that this is a volatile function which means that it will recalculate the resulting values each time a change occurs in the worksheet.
This means that if, after calculating the random numbers, you wish to keep the generated results, you will want to convert them into values.
How To Generate Random Numbers with the RAND Function
The RAND function can be used to generate a random number that is greater than zero and less than one.
This means that the result will be a decimal value that can repeat. However, this is unlikely due to the fact that it produces the values from a continuous range.
The formula for the RAND function is extremely simple:
= RAND( )
You do not need to enter any required or optional arguments in order to use this function.
The RAND function will always include simply an empty set of parentheses. In order to use the function to generate random numbers, simply follow these steps:
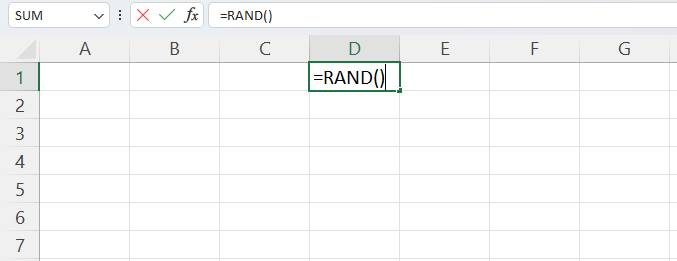
- Select the cells in which you wish to output the random numbers.
- Enter the formula =RAND() in the active cell.
- Hold down the “CTRL” key and click “Enter.”
- Random values will be generated in the selected cells.
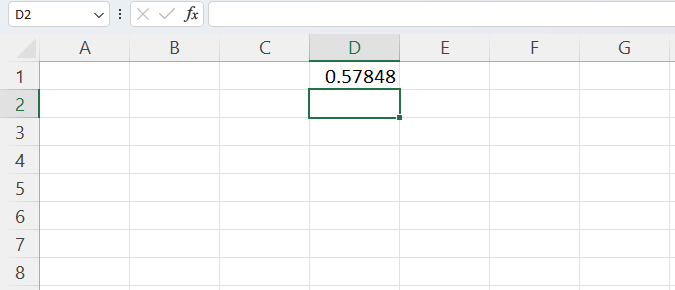
Like the RANDBETWEEN function, this is a volatile function, so if you want to prevent the values from being regenerated when changes are made in the worksheet, select the results and convert them to values.
As you can see, this formula is very easy to use.
However, in many cases, you may find decimal values less valuable than integers.
Though on its own, the RAND function cannot generate anything equal to or greater than one, it is possible to tweak the basic formula in order to generate larger results.
For example, if you need to generate a value between 1 and 100, you can adjust the formula like this:
=100*RAND()
This will simply multiply the result of the RAND formula to provide a decimal result between 0 and 100.
You can similarly adjust the formula to meet your required parameters, whatever they may be.
Unlike the RANDBETWEEN formula, this will produce decimal values that are far less likely to be duplicated due to the continuous range of decimal values the formula generates.
Using Microsoft’s Analysis ToolPak To Generate Random Numbers in Excel
Excel may not have a random number generator built-in, but Microsoft does offer an add-in named Analysis ToolPak that can perform a wide range of statistical functions, including generating random numbers.
Making Sure the Analysis ToolPak Add-in Is Installed
You can look under the “Analysis” section of the ribbon in the “Data” tab to check if you already have this add-in. But, assuming you haven’t already installed it, this probably is not the case.
Fortunately, this is easily solved by selecting “File,” “Options,” and then “Add-ins.”
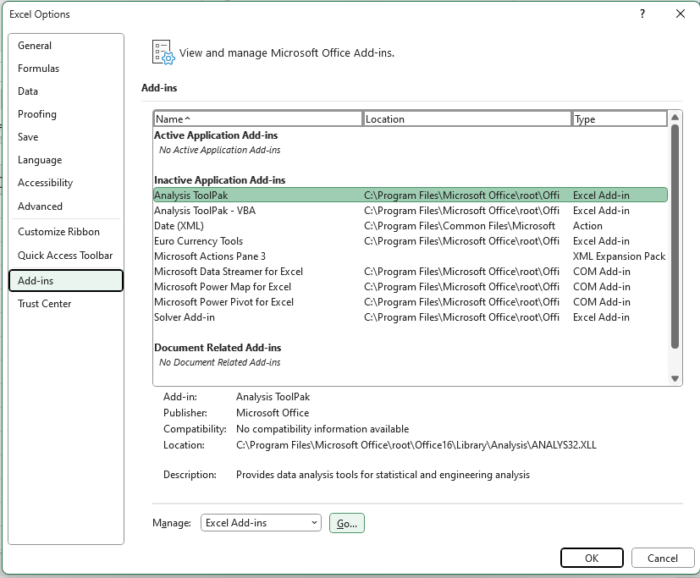
Here you can view and manage all of the add-ins you currently have installed.
At the bottom of the menu, you will see the “Manage” menu. Make sure that “Excel Add-ins” is selected, and then click go.
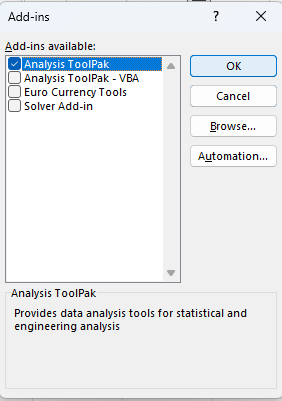
This will bring you to the “Add-ins” menu, where you can see all of the available add-in options for Excel.
Check the box to the left of “Analysis ToolPak” and select “OK” to add this tool to your ribbon.
Generating Random Numbers with the Analysis ToolPak
Once the Analysis ToolPak is installed, you can access it by navigating to the “Data” tab and selecting “Data Analysis” within the “Analysis” group.
This will bring up the “Data Analysis” dialog box, where you will find a long list of analysis tools available to use.
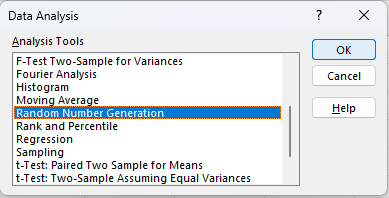
Scroll down the list until you see the option “Random Number Generation;” select this option and then “OK.”
This will bring up a new dialog box where you can set parameters for the random numbers it will generate.
You can start by selecting the number of columns to fill with the “Number of Variables” input and the number of rows with the “Number of Random Numbers” input.
If you leave these two boxes blank, the ToolPak program will simply input random numbers in the cells that you specify in the “Output Range” input below.
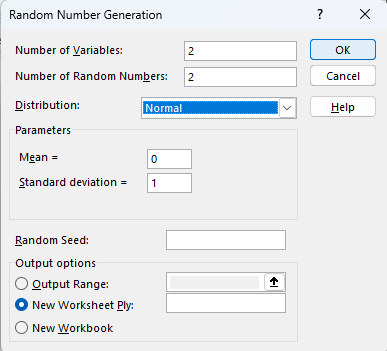
The random number generator provides an advanced list of options, including the distribution, which you can just leave to “Normal” if you wish, and a list of “Parameters,” which will update to reflect your selection in the “Distribution” box above.
You can also set “Random Seed” if you want the program to begin from a starting point of your choice.
You may also select “New Worksheet Ply” if you would like the random numbers to be generated into a new worksheet starting from Cell A1.
Likewise, you can select “New Workbook” to have the program place the results in a new workbook starting in cell A1.
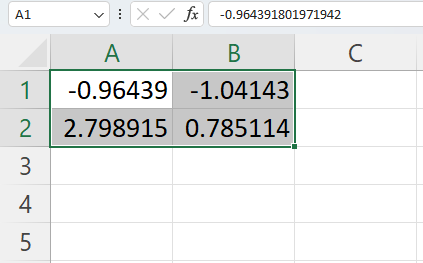
Once you are done making your selections, hit the “OK” button, and Excel will generate random numbers according to the parameters you have set.
Unlike the methods using the formulas above, these results are hardcoded, which means that they will not change when the worksheet is refreshed, and you will not need to convert them to values.
Using VBA Codes to Generate Random Numbers in Excel
VBA, or Visual Basic for Applications, is the programming language that supports most Microsoft Office applications, including Excel.
This is a powerful tool that can be used to emulate most of the tools we have discussed so far and more, but it takes some programming knowledge to make use of it.
VBA codes can be used to generate a random number, but this is a little more complicated than the previous methods.
Below you can see a relatively simple method of using VBA to generate some random numbers.
In itself, this has little more utility than the methods covered above.
However, with a bit of work and knowledge of how to manipulate it, you can gain much more flexibility and quickly generate random numbers whenever you need them by accessing your stored macros.
How to Generate Random Numbers with VBA
To get started, open the VBA menu from the “Developer” tab and select “Visual Basic” from the “Code” group.
This will open the VBA editor screen, and in the pane on the left, you will see all of the currently open workbooks and available sheets.
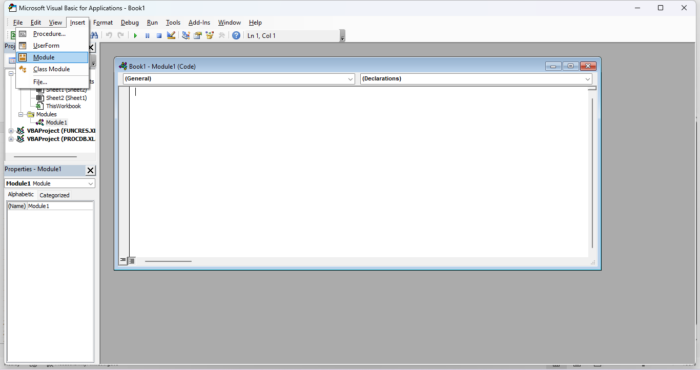
Click “Insert” on the top ribbon. This will open a dropdown menu where you will select “Module.” This will open a module window where you can enter the VBA code.
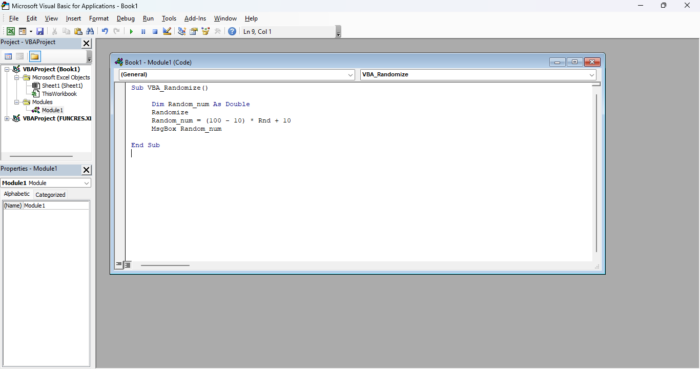
Enter the following formula substitution “Upper” and “Lower” with your desired parameters to generate a random number between two specified values:
Sub VBA_Randomize() Dim Random_num As Double Randomize Random_num = (Upper- Lower) * Rnd + Lower MsgBox Random_num End Sub
Once you enter the code, select “F5” or press the run icon to run your code.
Excel will display the result in a message box, and if you wish, you can then enter this number into a cell on your worksheet.
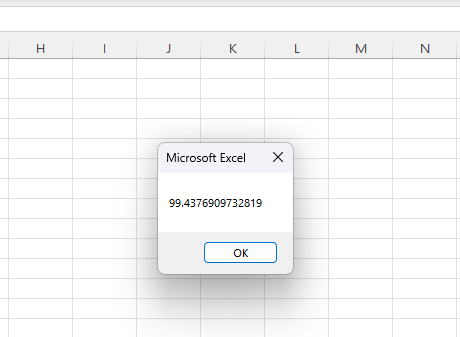
As you can see, this VBA code does not have the same utility as the methods above.
However, once you learn to use VBA codes effectively, you will see that there are a lot of different ways to use these formulas and alter them to suit your needs.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are a lot of ways to generate random numbers in Excel, and these are only the tip of the iceberg.
Whether you need to generate whole numbers, a range of numbers within upper and lower limits, or decimal values, Excel can get the job done.
Though the methods above are not the only ways to generate random numbers, they are some of the most convenient and can provide you with an effective way to generate random numbers for all of your needs, whether it is simulations, statistical analysis, or anything else.
