CONCATENATE Excel Range [With or Without Separator or Delimiter]Learn how to join multiple text strings together using the CONCATENATE and TEXTJOIN functions
When it comes to using data stored in Excel, the structure does not always come to align how you would like.
Often times you may need to split up entire cells and columns, and in many cases, you may need just the opposite, and this is where the CONCATENATE function comes in.
With the CONCATENATE function, we can combine values contained in multiple cells into one cell without merging the cells themselves.
This is often used to join text strings, such as multiple individual components of an address stored in different cells together.
Here we are going to see how you can use CONCATENATE to join an Excel range both with and without using a separator or delimiter.
What You Must Do To CONCATENATE on Your Excel Sheet
- You need one “text” feature at minimum to use the Excel CONCATENATE function
- If desired, you may concatenate as many as 255 strings totaling 8,192 characters.
- When you perform the CONCATENATE function, your result will always come out as a text string, in spite of all the source values being numbers.
- The Excel CONCATENATE function won’t work with arrays–you must list every cell reference individually. This would look like CONCATENATE(C4, C5, C6), not like CONCATENATE(C4:C6).
You will receive a #VALUE! Error if any of your arguments are not valid.
How To Use CONCATENATE Without a Separator
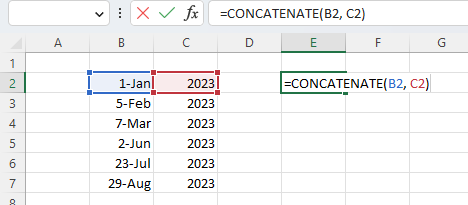
In its most basic form, it is extremely simple to use the CONCATENATE function.
In order to combine the values of two cells using the CONCATENATE function, all you will need to do is use the formula: =CONCATENATE(A1, B1), substituting your own cell references in place of these.
This will join the values of the two cells without any delimiters. In order to use CONCATENATE to join multiple cell values, each cell reference will need to be included in the formula regardless of whether they are contiguous or not.
This would look like: =CONCATENATE(A1, B1, C1).
Keep in mind that the values will be automatically formatted as a text string.
If you would like the result as a number, you can manually select each cell and change the formatting from the ribbon.
Alternatively, you could multiply the resulting output by 1.
How To Use CONCATENATE With a Delimiter
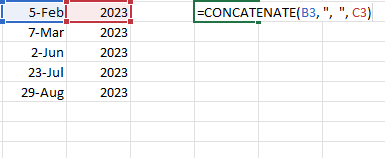
Here is how to use CONCATENATE to join a range with a delimiter.
Often times you may need to join values while separating them with some type of punctuation mark, such as a comma, hyphen, or slash.
Fortunately, this is easy to do simply by including your desired character into the formula you will use to tell Excel how to join two pieces of text.
A delimiter can be just about any consistently used symbol, including commas, hyphens, and even spaces.
In this case, we will use a comma as a delimiter to demonstrate how it works.
- Select a blank cell where you would like the result to be located.
- Enter the formula: =CONCATENATE(A1, “, “, B1). Do not forget to enclose your desired character within quotation marks.
- Run the formula and make sure your result is correct.
As you can see, it is easy to include an additional character in your result, and this can be particularly useful when converting data such as dates and addresses from a spreadsheet into a usable form.
Using CONCATENATE To Join Text and Cell Values
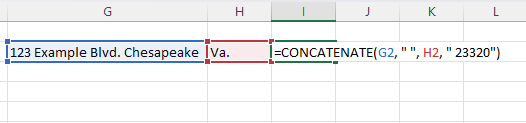
Notably, you can also use the CONCATENATE function to join cell values with text strings, which can be convenient for making the resulting string more useful.
This could be used, for example, to add a zip code to an existing address.
For example, using the formula =CONCATENATE(F1,” “, G1, “23320”) we can join cells containing a street address, city, and state while adding the zip code to create a complete address.
Simply enclose the value you would like to add in quotation marks just like you would a delimiter.
Using TEXTJOIN To Merge Multiple Cell Values
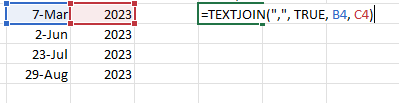
In the most recent editions of Excel, including Excel 2019 and Excel 365, Microsoft has given a newer, updated option for merging multiple strings, which can be a particularly flexible and easy-to-use tool.
For those with these newer editions, this function will often be the better choice for combining text from multiple cells.
The syntax for the TEXTJOIN function is:
TEXTJOIN( delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [ text2, … text_n ]
In this formula, the arguments are:
- delimiter: This is a text string that can either be empty or include one or more characters. It must be enclosed in quotation marks or include a reference to a cell that includes a valid text string.
- ignore_empty: If this is TRUE, it will ignore empty cells.
- text1, text2…: These are the text items to be joined and can include cell references containing valid values, text strings, or a range of cells. In total, you can include a maximum of 252 text strings that can be merged.
You can simply substitute in your cell references or text as well as a delimiter, if any, and this function will join it into your selected cell. This is easy to use and, for those with newer editions of Excel, more likely to be supported moving into the future.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned how to join multiple text strings together using the CONCATENATE and TEXTJOIN functions.
This can be a powerful tool for restructuring data, adding separators, and making it more useful for a wide range of applications.
